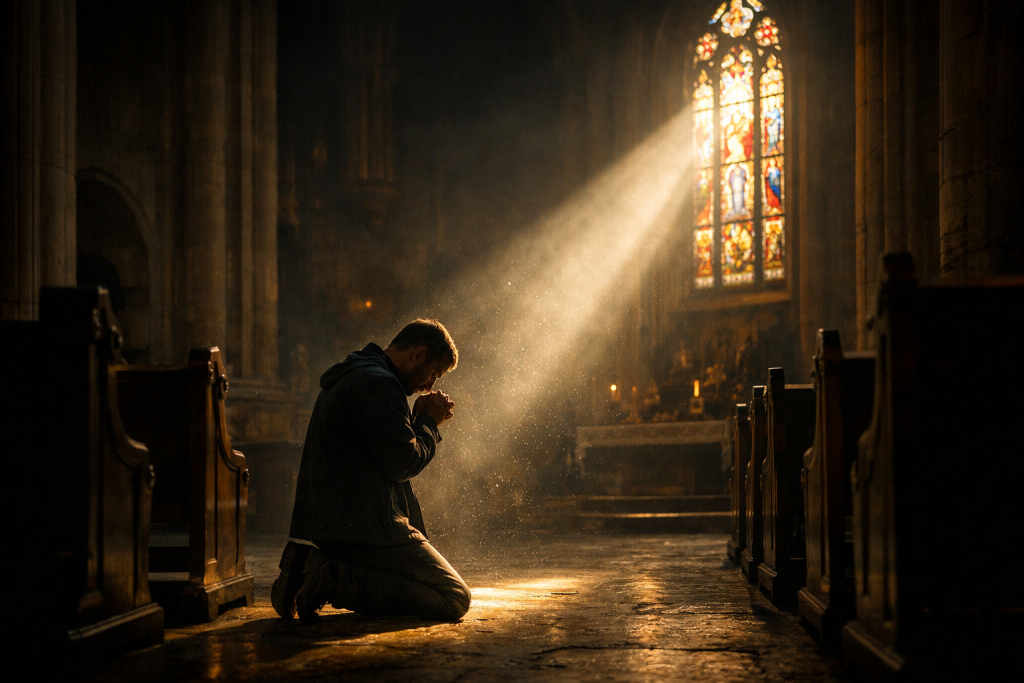
A moment of religious devotion can feel like a direct encounter with the divine — but the experience may have deeply human origins.
There are few experiences in human life more convincing than religious conversion.
In the moment it happens, it feels absolute.
The new believer does not merely adopt a belief; he experiences what appears to be a profound transformation of reality itself. The world suddenly becomes charged with meaning. Events seem purposeful. Personal history acquires a narrative arc. Even suffering can appear reinterpreted as part of a divine plan.
To the convert, the conclusion feels unavoidable: God has revealed Himself.
I know this experience from the inside. For several years I believed, with complete sincerity, that God had personally intervened in my life. The sense of transformation was overwhelming. At the time it felt impossible to doubt that something supernatural had occurred.
The experience is often accompanied by powerful emotions: relief, gratitude, awe, sometimes tears. The convert may describe feeling “known,” “forgiven,” or “reborn.” For many, this moment becomes the central turning point of their life story.
From the inside, the experience feels like the discovery of truth. God exists. Faith becomes certainty (Hebrews 11:1).
From the outside, however, something more complex is happening.
A psychological ignition
Modern psychology offers a more prosaic explanation for the intensity of conversion.
Many conversions occur at moments of emotional vulnerability: crisis, guilt, loneliness, addiction, grief, or identity confusion. In such moments the mind becomes unusually receptive to radical reinterpretations of reality.
These states create a powerful readiness for cognitive re-organisation. The mind searches urgently for a coherent narrative capable of resolving internal tension.
Religious frameworks are uniquely suited to provide such narratives. They offer a ready-made interpretation of suffering, a clear moral structure and the promise of forgiveness and life beyond the grave.
When the new believer accepts this framework, the psychological relief can be immense. The sense of personal chaos suddenly resolves into a meaningful story.
The experience feels supernatural.
In reality, it may simply be the human mind discovering an interpretation that temporarily stabilises itself.
The sociological amplifier
But psychology alone does not explain the power of conversion.
The social environment plays an equally decisive role.
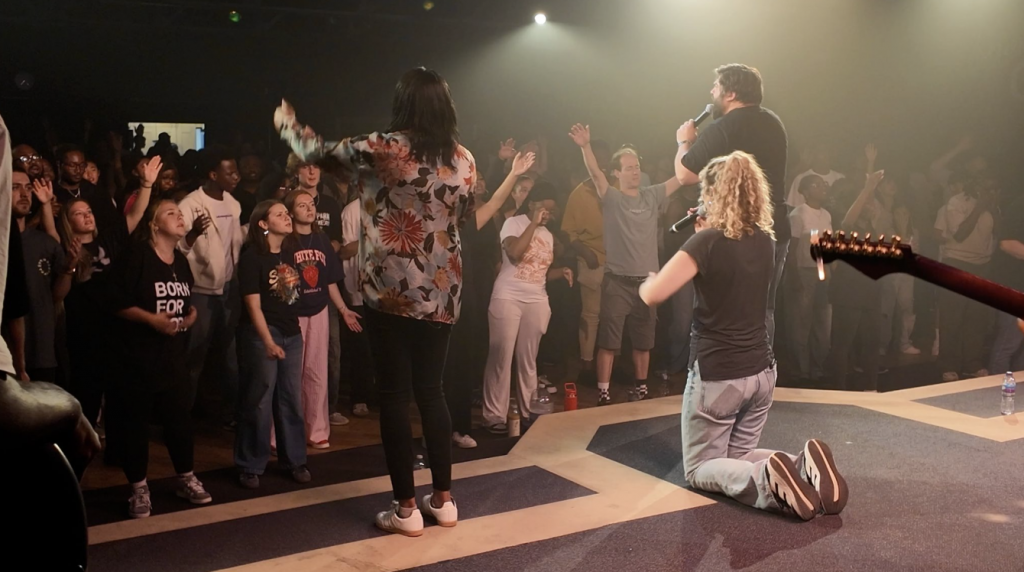
Conversion rarely happens in isolation. It usually occurs within communities already organised around the expectation of transformation. Worship services, testimonies, music, prayer and communal affirmation together create a powerful emotional ecosystem.
When a convert stands before such a community and declares a new faith, the response is immediate: approval, celebration, belonging.
The individual does not simply gain a belief.
He gains a new identity and a new tribe.
Human beings are exquisitely sensitive to social reinforcement. Once a community confirms that a person has been “saved,” the psychological commitment deepens rapidly. Doubt becomes socially costly. Certainty becomes a badge of belonging.
Belief, in this sense, is stabilised not only internally but collectively.
The sincerity paradox
None of this means that conversion experiences are insincere.
Quite the opposite.
At the moment of conversion, the belief is usually completely genuine. The emotional intensity is real. The sense of transformation is real. The feeling of encountering God is real.
But sincerity does not guarantee accuracy.
Human beings are capable of deeply authentic experiences that nevertheless rest upon mistaken interpretations of reality.
Religious conversion may be one of the most powerful examples of this phenomenon.
Human beings are capable of deeply authentic experiences that nevertheless rest upon mistaken interpretations of reality.
The problem of competing revelations
One further observation complicates the picture.
If religious conversion truly revealed a universal divine reality, we might expect converts around the world to converge toward the same understanding of God.
Instead, the opposite happens.
Christians experience conversions that confirm Christianity.
Muslims experience conversions that confirm Islam.
Hindus encounter Krishna.
Pentecostals encounter the Holy Spirit.
Catholics encounter the Virgin Mary.
Each experience feels equally convincing to the person undergoing it.
The simplest explanation is not that all these mutually contradictory revelations are true.
It is that the human mind is capable of generating profoundly convincing experiences within whatever symbolic framework it inhabits.
The quiet aftermath
For some people, the story ends with lifelong faith.
For others, something else happens.
Years later, the convert begins to recognise the psychological and sociological forces that once felt invisible. The experience that once seemed supernatural begins to look more recognisably human.
This realisation can be unsettling.
Because it means confronting a difficult possibility:
The God who once felt unquestionably real may have been a projection created by the deepest needs of the human mind.
And yet the experience itself — the hope, the meaning, the transformation — was never fake.
It was simply human.
“The gods we worship write their names on our faces.”
— C. G. Jung


 Every organisation has a bell curve.
Every organisation has a bell curve.